
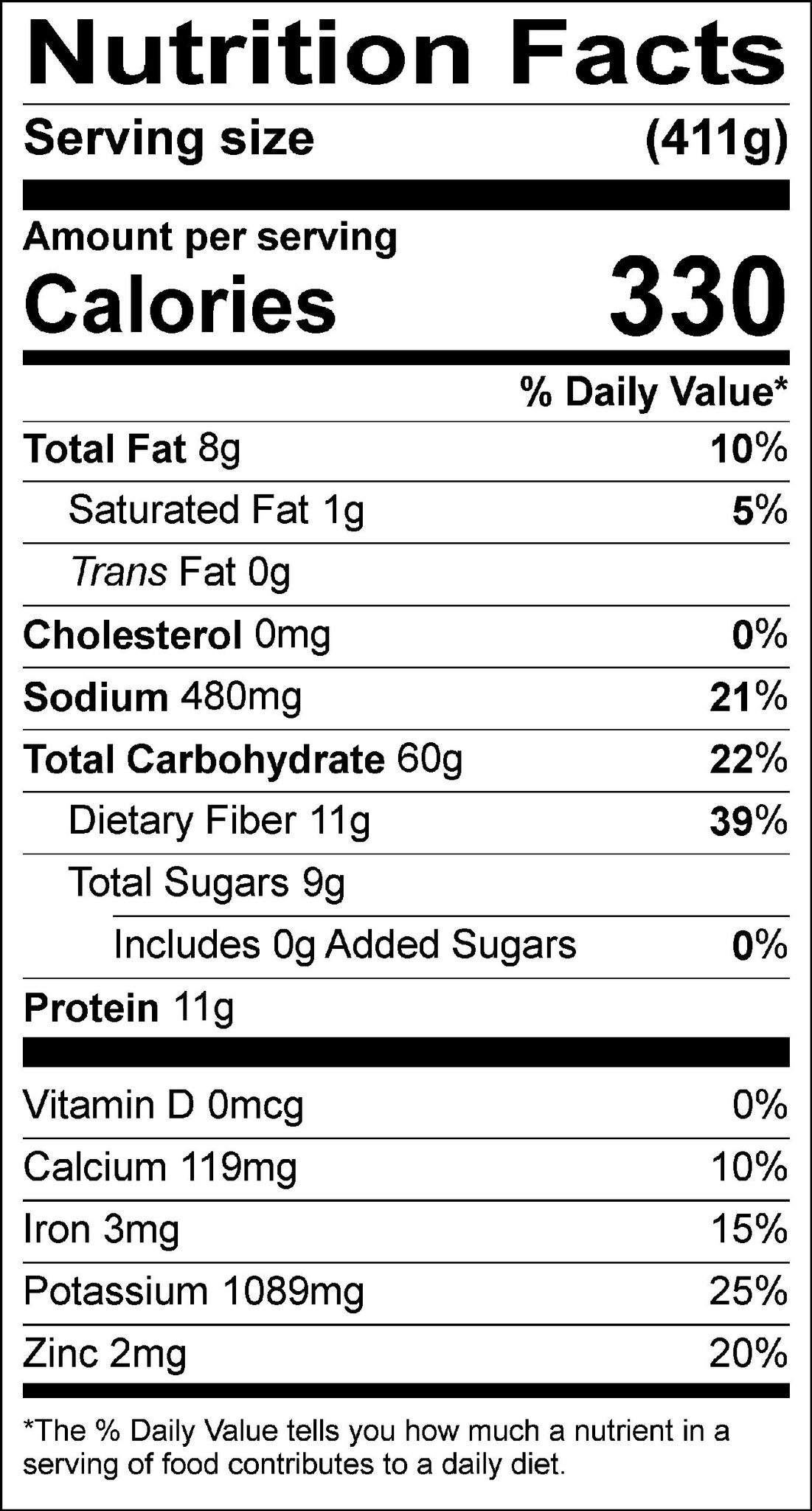
Vitamin C strengthens the immune system by encouraging the body to produce more white blood cells and protecting against oxidative stress ( 22, 23). Supports immunityĪcorn squash is an excellent source of vitamin C, a nutrient well-known for its beneficial effects on immunity ( 1). This allows blood vessels to relax and lowers blood pressure ( 20).Īccording to one study, each 100 mg increase in magnesium intake was linked with a 5% reduction in hypertension risk ( 21). Magnesium lowers blood pressure in part by acting similarly to a group of medications, known as calcium channel blockers, that are used to treat hypertension ( 19).Ĭalcium channel blockers reduce the amount of calcium entering smooth muscle cells in the blood vessel walls. Potassium is a mineral that counteracts the effects of sodium on blood pressure by stimulating the kidneys to excrete more sodium in the urine ( 17).Ĭonsuming at least 3500 mg of potassium each day significantly lowers blood pressure in people with hypertension ( 18). Having too much water in your blood increases the amount of pressure that’s exerted on blood vessel walls ( 15).Īlthough research is mixed, evidence suggests that reducing sodium intake may help lower blood pressure in some people, particularly those who are “salt sensitive” ( 16). Sodium can raise blood pressure by pulling water into the bloodstream. May lower blood pressureĪcorn squash is naturally low in sodium and high in potassium and magnesium, a combination that may help protect against hypertension (high blood pressure) ( 1). Regardless of its glycemic index, acorn squash can be enjoyed as part of a balanced meal alongside protein and fat to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. This means that it causes a slow and steady rise in blood sugar. However, a similar vegetable - butternut squash - has a glycemic index of 51, which is considered low ( 14). We weren’t able to find any research on acorn squash’s glycemic index, a measure of how quickly a food causes blood sugar levels to rise ( 13). This important hormone allows sugar in the blood to move into cells where it can be used for energy ( 12). It is also high in nutrients, including magnesium and vitamin B6, that help regulate the secretion of insulin ( 10, 11). Regulates blood sugarĪcorn squash is a great source of complex carbohydrates, which take longer to digest and result in a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels ( 9).

Consuming a variety of high-fiber foods, including acorn squash, can help you meet your needs. Most people in the United States only get about half of the recommended amount of fiber ( 8). These bacteria produce beneficial compounds like short-chain fatty acids, which strengthen the intestinal barrier and lower inflammation ( 4, 5).ĭiets high in fiber, like the kind found in acorn squash, are also linked with lower rates of colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease ( 6, 7). Some types of fiber even help increase the number and variety of good bacteria living in the gut. Improves digestive healthĪcorn squash is higher in fiber than most other winter squash, offering a whopping 9 grams per cooked cup - that’s nearly one-third of the DV ( 1, 2).įiber can reduce symptoms of constipation and keep the digestive system running smoothly by adding bulk to the stool and increasing the frequency of bowel movements ( 3). One cup (205 grams) of cooked acorn squash provides the following nutrients ( 1):Ī single one-cup serving of acorn squash can help you meet close to one-quarter of the Daily Value (DV) for thiamin, vitamin C, vitamin B6, manganese, magnesium, copper, and pantothenic acid ( 2). High in nutrients and antioxidantsĪcorn squash is a nutrient-dense vegetable high in essential vitamins and minerals, as well as fiber.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
